
Sinus bradycardia and heart rate variabilityĪltered ion channel and transporter expression and traffickingĪltered ventricular myocyte energetics leading to glycogen-engorged vacuoles and disruption of annulus fibrosus Specification defect of the atrioventricular node and the ventricular cardiac conduction systemĪtrioventricular block, bundle-branch blockĪltered nuclear stress mechanics and hyperactivation of MAPK signaling Sinus bradycardia, atrioventricular block, bundle-branch block Impaired myocyte coupling resulting in slowed conduction Sinus node dysfunction, atrioventricular block, atrial standstillĪltered Ca 2+ handling likely affecting the Ca 2+ clock Prolongation of action potential duration and reduced cardiac excitability Reduced cardiac excitability and slowed conduction loss of depolarizing current in peripheral sinoatrial node cellsĪtrioventricular block, bundle branch block Sick sinus syndrome, progressive cardiac conduction defect, atrial standstill, atrioventricular block, bundle branch block Genetic Basis of Conduction System Disease Gene Name We also investigate evolving therapeutic strategies that may serve as adjuvant or replacement therapy to current implantable pacemakers. In this review, we discuss gene families that have been implicated in human CCS diseases of rhythm, conduction block, accessory conduction, and development ( Table). Applying a multidisciplinary approach, which includes human genetic screening, biophysical analysis, and transgenic mouse technology, has yielded a broad array of gene families involved in maintaining normal CCS physiology ( Figure 1). Inherited forms of CCS disease are rare, but each new mutation provides invaluable insight into the molecular mechanisms governing CCS development and function. CCS dysfunction is primarily due to acquired conditions such as myocardial ischemia/infarct, age-related degeneration, procedural complications, and drug toxicity. Human diseases of the conduction system have been identified that alter impulse generation, impulse propagation, or both.
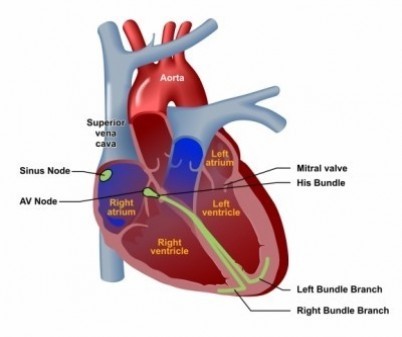
The functional components of the CCS can be broadly divided into the impulse-generating nodes and the impulse-propagating His-Purkinje system.

The human heart beats 2.5 billion times during a normal lifespan, a feat accomplished by cells of the cardiac conduction system (CCS). Customer Service and Ordering Information.Stroke: Vascular and Interventional Neurology.Journal of the American Heart Association (JAHA).Circ: Cardiovascular Quality & Outcomes.Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology (ATVB).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
